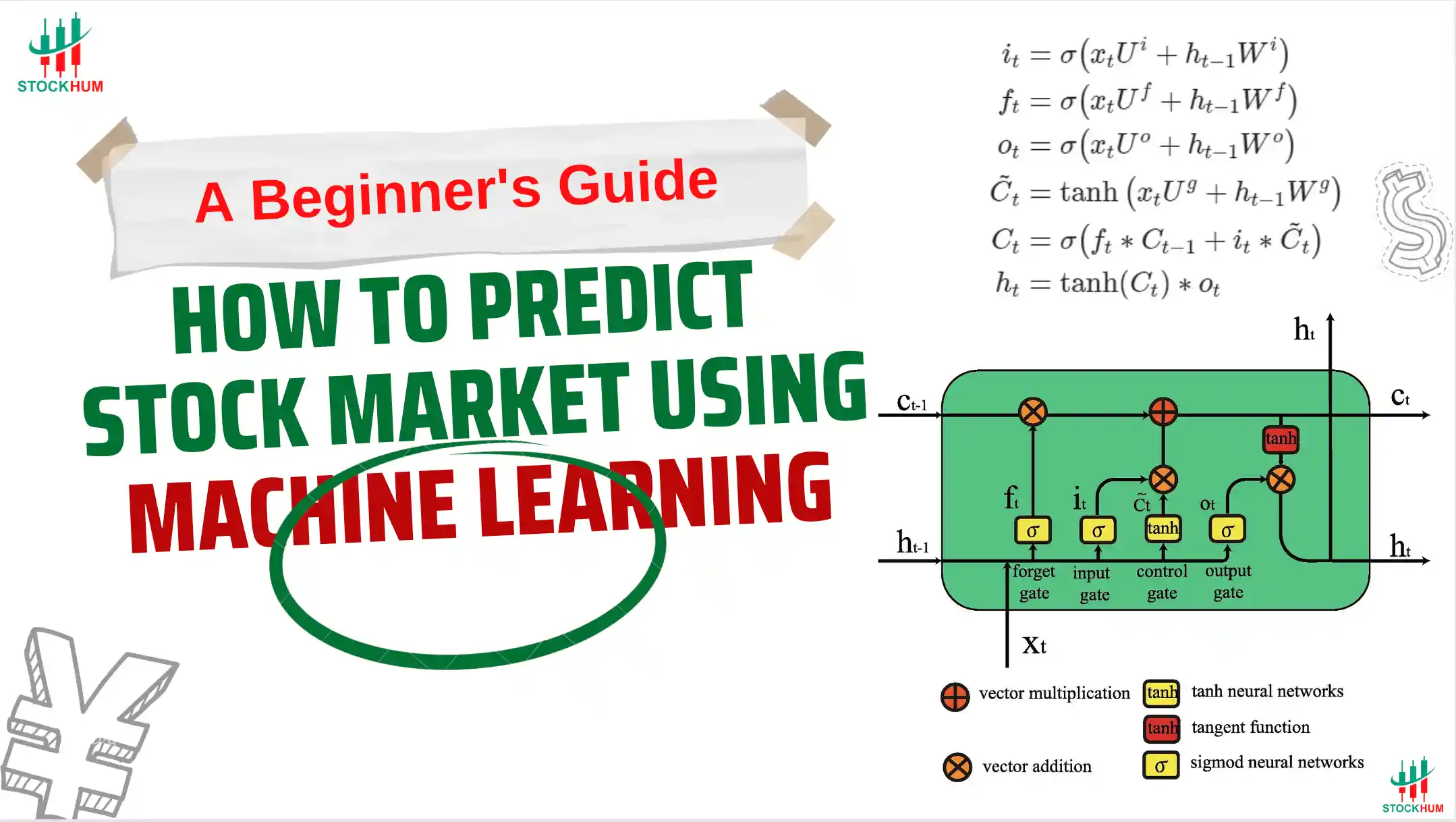
In this Article
In the vast geography of finance, the US Stock Market Historical Trend stands as a charming journey through the highs and lows of the American economy. Over time, this fiscal rollercoaster has woven a fascinating narrative of triumphs, challenges, and adaptability.
The US stock market historical trend last 100 years offers a perception of the nation’s economic development. It reflects the impacts of vital events similar to wars, profitable crises, and technological revolutions.
From the buoyant sanguinity of the Roaring Twenties to the crash of 1929 and the posterior Great Depression, the stock market has survived storms that have shaped both Wall Street and Main Street.
The post-World War II period brought about a period of unknown growth and substance, known as the “Golden Age,” while the dot-com smash of the late 20th century showcased the power of invention.
This article digs into a detailed explanation of the US stock market historical trend last 100 years. We will explore how it glasses the broader historical context and influences the financial landscape. Join us as we unravel the vestments of time, examining the triumphs and agonies that have tagged the journey of the US stock market over the decades.
Historical Period of the US Stock Market
The US Stock Market, a foundation of the nation’s profitable system, has a rich history that began with its establishment and development in the early times. This section describes the origins, growth, and early mileposts that shaped the foundation of the market.
Establishment and Development
Arising in 1790, the Philadelphia Stock Exchange marked the commencement of the US stock market, driving a severe profitable downturn that eroded stock prices and investor confidence. Still, the Buttonwood Agreement of 1792 marked the birth of systematized trading in New York City. This agreement, linked under a buttonwood tree on Wall Street, laid the root for what would later become the New York Stock Exchange( NYSE).
Key Mileposts in the 19th Century
In the 19th century, significant milestones propelled the US stock market forward. One of the most noteworthy events was the formal creation of the New York Stock and Exchange Board in 1792, which ultimately evolved into the NYSE. As the market continued to develop, the telegraph’s preface in the 1830s eased brisk communication, enabling investors to admit and act on market information more efficiently.
Impact of Economic Events on Early Trends
Economic events played a vital part in shaping early stock market trends. The fear of 1837, touched off by a fiscal extremity and bank crashes, profoundly affected the US economy and the stock market. The impacts of the fear of 1837 underlined the interconnectedness between profitable events and stock market trends during the early years of the US Stock Market’s actuality.
Its establishment marked the early times of the US Stock Market, crucial mileposts in organizational development, and the profound influence of profitable events on shaping its original trends. These foundational rudiments set the stage for the request’s continued elaboration and growth in the following centuries.
The Roaring Twenties and the Great Depression
Prosperity and Bull Market
The 1920s, generally known as the Roaring Twenties, witnessed unknown substances in the U.S. A booming stock market characterized this period, fueled by inventions, increased artificial products, and a surge in consumer spending.
The sanguinity was reflected in a prolonged bull market, where stock prices constantly rose, attracting enthusiastic investors eager to subsidize the apparent fiscal wealth. The Roaring Twenties marked a period of vibrance and profitable growth that significantly impacted the literal trend of the US Stock Market.
Stock Market Crash of 1929
The peak of the Roaring Twenties suddenly ended when the Stock Market Crashed in 1929. A capstone of factors, including excessive enterprise, overrated stocks, and an unforeseen loss of investor confidence, led to a disastrous market collapse.
On October 29, 1929, known as Black Tuesday, stock prices dropped, causing significant financial losses and leading to the Great Depression. This vital event, a stark reversal from the earlier sanguinity, played a defining part in shaping the literal trend of the US Stock Market, marking the morning of a prolonged period of profitable difficulty.
Effects of the Great Depression on Stock Market Trends
The Great Depression profoundly impacted stock market trends, reshaping the market structure and investor conduct. The prolonged profitable downturn led to a severe job market, with stock prices sinking to unknown lows. Investor confidence eroded, and the prevailing trend became with caution and threat aversion.
Government intervention and nonsupervisory measures were enforced to stabilize the market. The effect of the Great Depression left an enduring imprint on the literal trend of the US Stock Market, emphasizing the vulnerability of fiscal markets to systemic shocks and the need for safeguards to help a rush.
Post-WWII Period and Economic Blast
Recovery and Growth
Following the conclusion of World War II, the United States endured a remarkable period of post-war recovery and profitable expansion. The GI Bill, aimed at abetting veterans’ reintegration, and a wave in artificial products contributed to robust, profitable growth.
The returning fighters fueled a casing smash, while increased consumer spending became a driving force. This post-WWII period marked a transition from wartime austerity to profitable substance, setting the stage for significant changes in the literal trend of the US Stock Market.
Part of Government Policies
Government policies played a vital part in fostering the post-WWII profitable smash. The Marshall Plan handed aid to war-destroyed European nations, creating new import markets for American goods. Also, policies promoting structure development and scientific exploration bolstered invention.
The Federal Reserve enforced friendly financial policies, contributing to low interest rates and easing borrowing. These combined efforts by the government stimulated profitable growth, impacting the literal trend of the US Stock Market by creating a conducive context for investment and expansion.
Notable Things Shaping Stock Market Trends
Several notable events during the post-WWII period significantly changed stock market trends. The oil painting prescription of the 1970s, touched off by geopolitical pressures, led to a shaft in oil painting prices and initiated a period of stagflation.
This event profoundly impacted the stock market, causing volatility and altering investor prospects. Also, other significant events, such as the end of the Bretton Woods system and the posterior adoption of floating exchange rates, further shaped the literal trend of the US Stock Market by introducing new dynamics and challenges for investors to navigate a rush.
Challenges and Volatility in the Late 20th Century
Oil Crisis and Economic Downturns
The late 20th century brought onward challenges that tested the adaptability of the US Stock Market. The oil extremity of the 1970s, touched off by geopolitical pressures in the Middle East, led to a wave in oil prices.
This bouleversement resulted in profitable downturns, high affectation, and reduced consumer spending, inclusively impacting the stock market. The challenges posed by the oil extremity underlined the interconnectedness of global events and their capacity to impact the historical trend of the US Stock Market.
Technological Breakthroughs and Dot-Com Bubble
Technological creations in the late 20th century, particularly the rise of the internet, marked a transformative period for the US Stock Market. The late 1990s saw the dot-com bubble, characterized by an unknown wave in the stock prices of internet-grounded companies.
The speculative distraction outpaced sound fundamentals, performing in the bubble’s burst in the early 2000s and substantial market corrections. This period stressed the impact of technological invention on market dynamics and demonstrated the need for a conservative approach to investment in fleetly evolving sectors.
Impact of Global Events on Stock Market Trends
The late 20th century was characterized by increased globalization, bringing new challenges to the US Stock Market. Geopolitical pressures and global events, similar to the end of the Cold War and indigenous conflicts, had far-reaching consequences on market trends.
The interconnectedness of economies and fiscal markets became apparent, with stock prices responding to transnational developments. During this period, they emphasized the significance of considering global factors in understanding and predicting US Stock Market historical trends.
Recent Trends and Progresses
Recovery from the 2008 Crisis
The outcome of the 2008 fiscal extremity marked a period of recovery for the US Stock Market. Government interventions, encouragement packages, and nonsupervisory reforms played pivotal places in stabilizing the fiscal system.
The stock market traditionally rebounded, reaching new highs. Still, the recovery process disclosed lasting scars, affecting investor sentiment and trouble perceptions. Comprehending the dynamics of this recovery is pivotal for understanding the current historical trend of the US stock market.
Technological Inventions in Trading
Recent years have witnessed a wave of technological inventions revolutionizing stock market trading. Crucial basics like high-frequency Trading, algorithmic Trading, and the integration of artificial intelligence have become integral to market dynamics. These inventions have enhanced trading effectiveness, liquidity, and availability.
Still, they also pose challenges, similar to market volatility and the eventuality of systemic pitfalls. Exploring the impact of these technological advancements provides perceptivity into the evolving nature of the literal trend of the US Stock Market.
Globalization and its Influence on the US Stock Market
Globalization has played an eloquent part in shaping the recent trends of the US Stock Market. Accelerated interconnectedness with transnational markets has uncovered the US market to global profitable shifts and geopolitical affairs. Cross-border investments, foreign exchange influences, and the expansion of transnational corporations have all contributed to a more encyclopedia-sensitive stock market.
As trade walls abate, the influence of transnational factors on the literal trend of the US Stock Market has become more pronounced, substantiating the significance of a comprehensive global outlook for investors and market analysts.
Crucial Factors Impacting Historical Trends
Economic Pointers
Economic pointers play a pivotal part in impacting the literal trends of the US Stock Market. Pointers like Gross Domestic Product ( GDP) and affectation rates give perception into the economy’s overall health. Optimistic GDP growth frequently correlates with a bullish market, signaling profitable expansion and commercial profitability.
High affectation may raise enterprises’ buying power and impact market sentiment. Understanding these economic pointers helps investors anticipate market movements and make informed opinions. It highlights the essential relationship between economic fundamentals and the historical trend of the US Stock Market.
Political Events
Political events and policies exercise significant influence on the historical trends of the US Stock Market. Government opinions on financial and financial policies, trade agreements, and nonsupervisory architectures directly impact investor confidence. Elections, geopolitical pressures, and legislative changes can introduce queries, leading to market volatility.
Also, programs aimed at profitable encouragement or austerity shape market prospects. A comprehensive analysis of political events is essential for investors to anticipate potential market shifts. It comprehends the broader economic environment that contributes to the historical path of the US Stock Market.
Technological Advancements
Technological advancements have been a transformative force shaping the historical trends of the US Stock Market. From the arrival of electronic trading to the rise of algorithmic and high-frequency trading, technology has accelerated request conditioning and altered trading dynamics.
AAccurate-time information, online trading platforms, and artificial intelligence have enhanced request effectiveness and introduced new challenges similar to request volatility and cybersecurity pitfalls.
Understanding the impact of these technological inventions is vital for investors to navigate the evolving geography of stock trading. It is shaping the ongoing historical trend of the US stock market.
Long-Term US Stock Market Historical Trend
These charts show the enduring historical circles of crucial US Stock market indicators Dow Jones, S&P 500, NASDAQ, and NYSE — disclosing long-term trends that reflect the overall performance and elaboration of the US stock market.
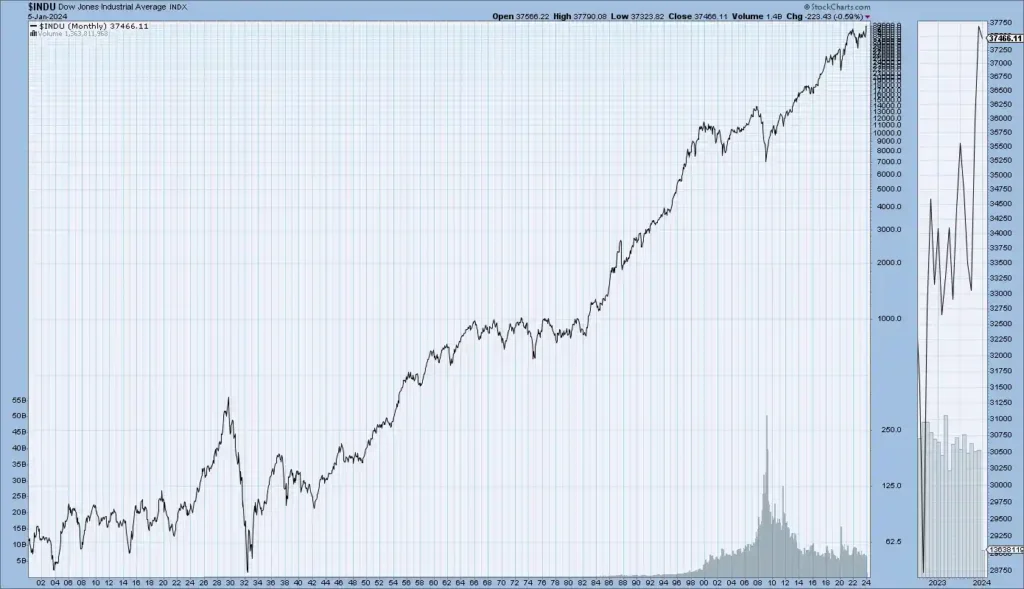
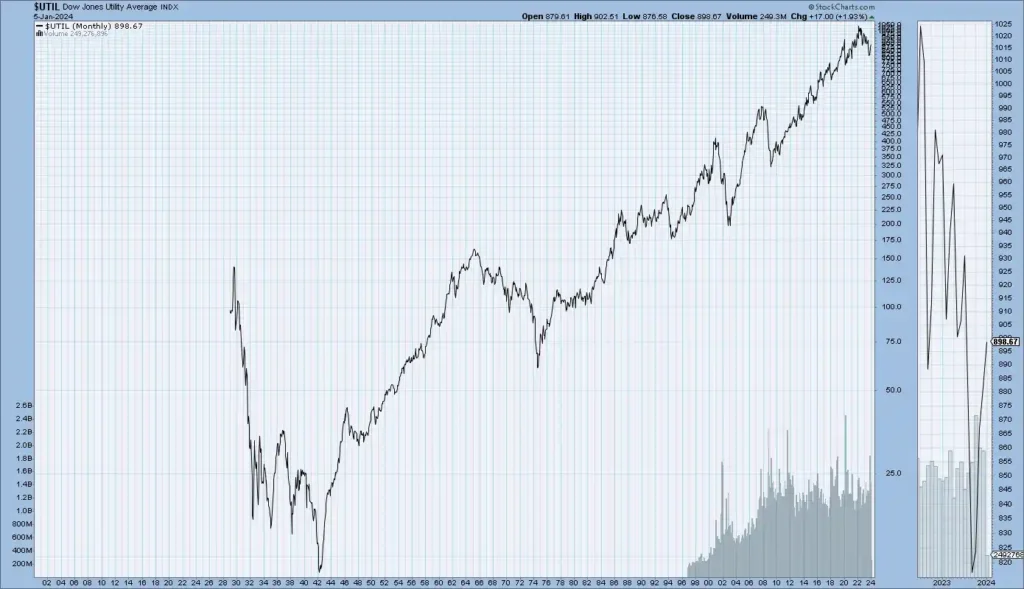
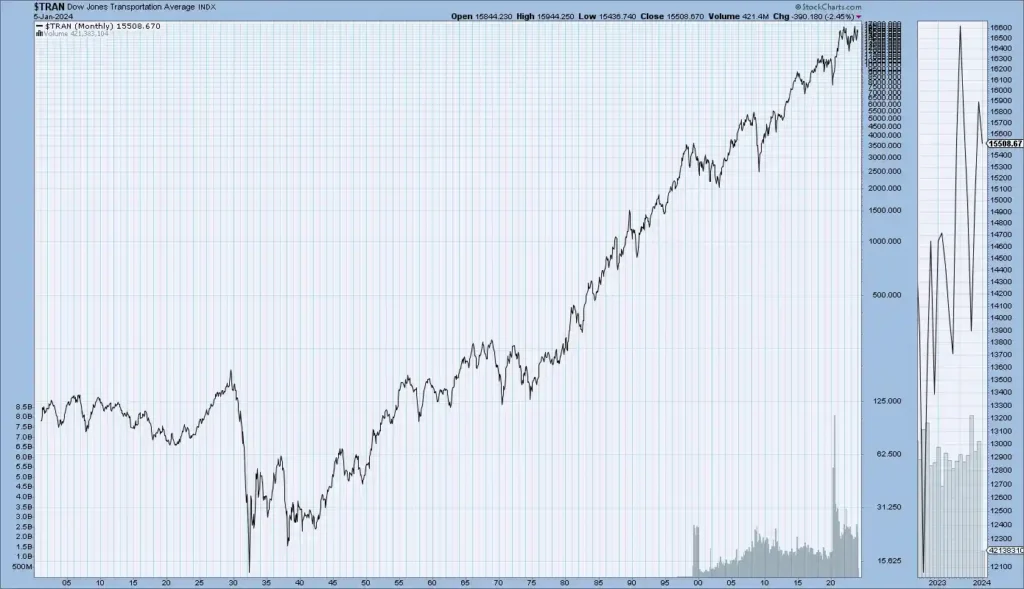
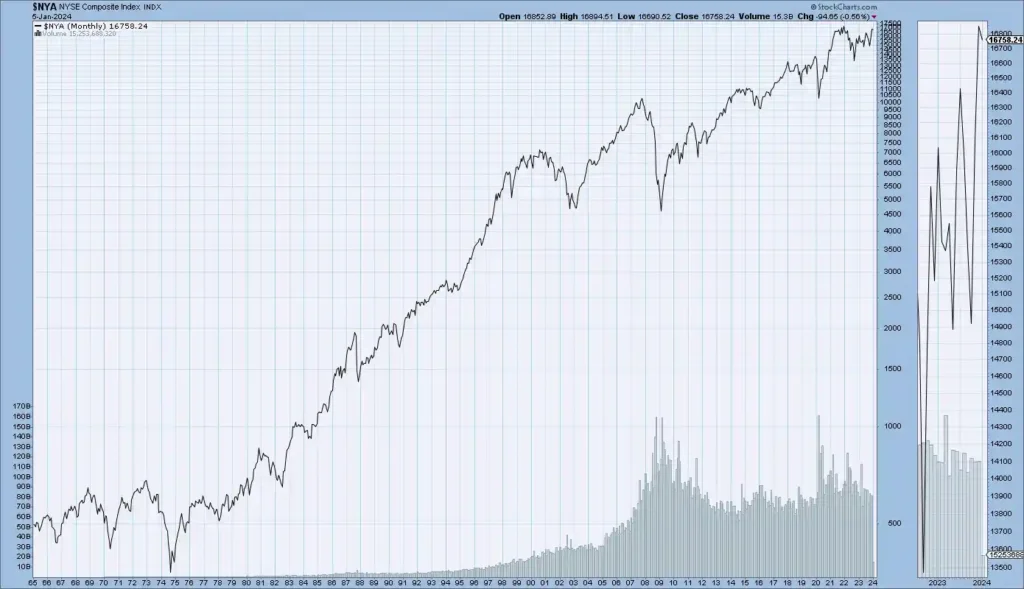
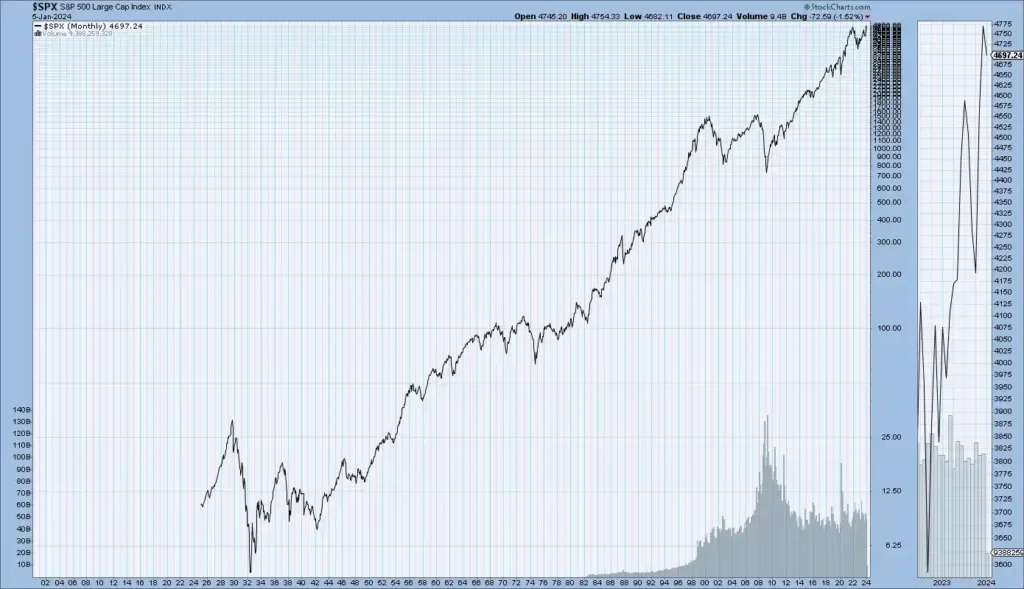
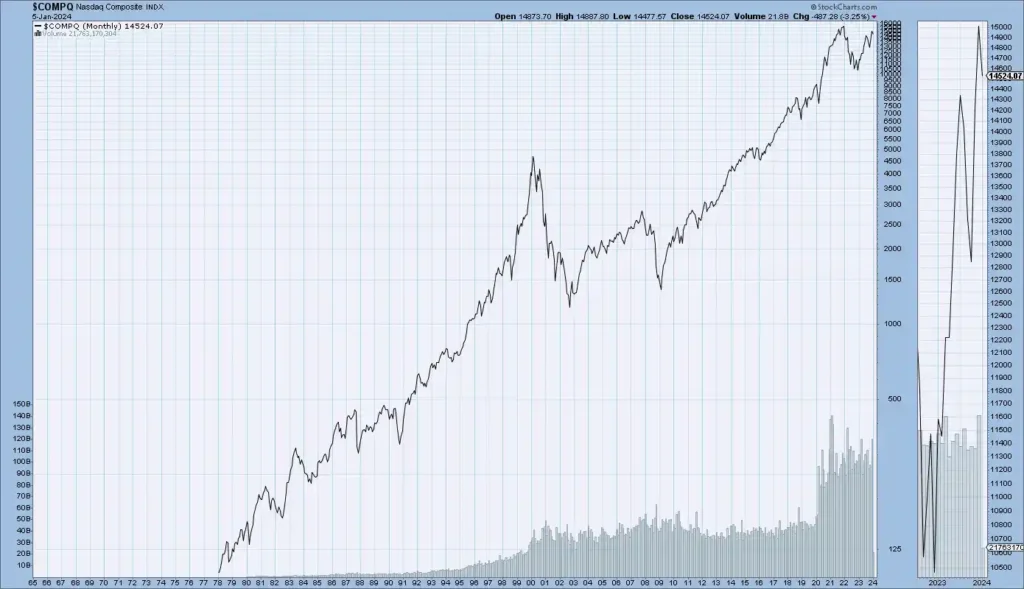
Dow Jones Historical Trend
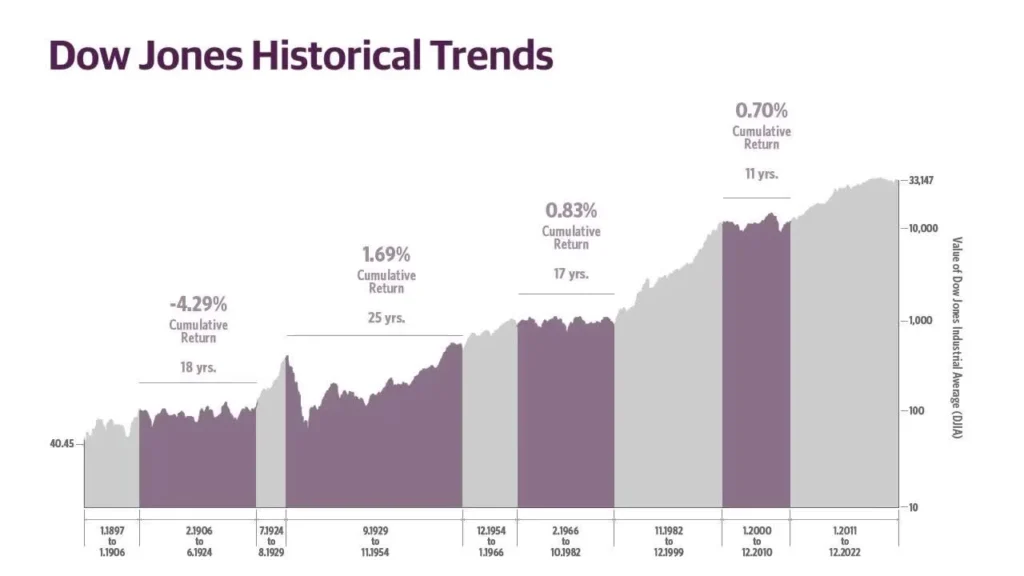
Secular Bull Market
In a secular bull market, the overall trend is overhead, characterized by consecutive high points that constantly better former peaks. This upward movement reflects sanguinity, profitable growth, and positive investor sentiment.
| Start | End | Months | Years | Annualized Return | Cumulative Return | Annualized Std. Dev. |
| 1.1.1897 | 1.31.1906 | 109 | 9 | 10.56% | 148.92% | 20.45% |
| 7.1.1924 | 8.30.1929 | 62 | 5 | 30.44% | 294.66% | 17.30% |
| 12.1.1954 | 1.31.1966 | 134 | 11 | 8.72% | 154.29% | 11.68% |
| 11.1.1982 | 12.31.1999 | 206 | 17 | 15.34% | 1,059.31% | 15.02% |
| 1.1.2011 | 12.31.2022 | 144 | 12 | 9.16% | 186.31% | 14.43% |
Secular Bear Market
The overall trend is over in a secular bear market, marked by high points that fail to exceed former peaks. This patient decline reflects extended pessimism, economic challenges, and negative investor sentiment, leading to a prolonged period of market value reduction.
| Start | End | Months | Years | Annualized Return | Cumulative Return | Annualized Std. Dev. |
| 2.1.1906 | 6.30.1924 | 221 | 18 | -0.24% | -4.29% | 18.54% |
| 9.1.1929 | 11.31.1954 | 303 | 25 | 0.07% | 1.69% | 24.96% |
| 2.1.1966 | 10.31.1982 | 201 | 17 | 0.05% | 0.83% | 15.25% |
| 1.1.2000 | 12.31.2010 | 132 | 11 | 0.06% | 0.70% | 15.75% |
S&P 500 Historical Trends
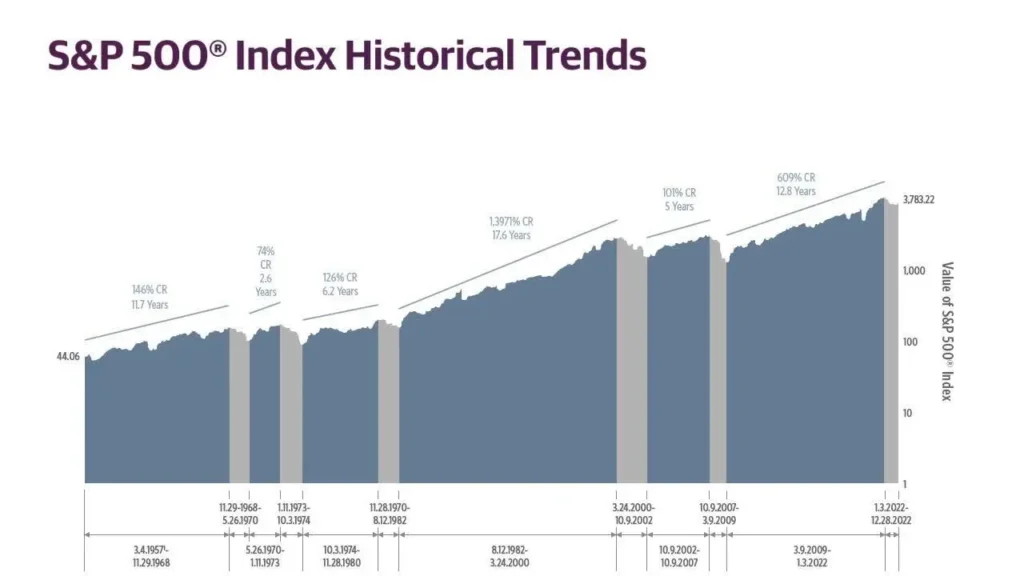
Secular Bull Market
| Start | End | Months | Years | Annualized Return | Cumulative Return | Annualized Std. Dev. |
| 3.4.1957 | 11.29.1968 | 140 | 11.7 | 8.0% | 146.0% | 10.0% |
| 5.26.1970 | 1.11.1973 | 31 | 7.4 | 23.8% | 73.5% | 11.3% |
| 10.3.1974 | 11.28.1980 | 73 | 6.2 | 14.3% | 125.6% | 13.6% |
| 8.12.1982 | 3.24.2000 | 211 | 17.6 | 16.6% | 1,391.4% | 16.0% |
| 10.9.2002 | 10.9.2007 | 60 | 5.0 | 15.0% | 101.5% | 13.6% |
| 3.9.2009 | 1.3.2022 | 153 | 12.8 | 16.6% | 609.0% | 17.7% |
Secular Bear Market
| Start | End | Months | Years | Annualized Return | Cumulative Return | Annualized Std. Dev. |
| 11.29.1968 | 5.26.1970 | 17 | 1.5 | -27.1% | -36.1% | 11.4% |
| 1.11.1973 | 10.3.1974 | 20 | 1.7 | -32.6% | -48.2% | 17.9% |
| 11.28.1980 | 8.12.1982 | 20 | 1.7 | -17.3% | -27.1% | 13.8% |
| 3.24.2000 | 10.9.2002 | 30 | 2.5 | -23.7% | -49.1% | 22.9% |
| 10.9.2007 | 3.9.2009 | 17 | 1.4 | -44.7% | -56.8% | 37.9% |
| 1.3.2022 | 12.28.2022 | 11 | 1.0 | -22.8% | -21.1% | 24.2% |
Conclusion
Retracing the steps of the US Stock Market’s historical trip, we witness a shade woven with adaptability, growth, and inevitable challenges. From its nascent establishment to the tumultuous times of the Great Depression and the posterior reclamations, the market has survived multitudinous storms, each leaving an unforgettable mark on its historical trend.
Learning from this intricate history becomes a compass for ultramodern investors. The echoes of profitable pointers, political events, and technological revolutions resonate through time, offering pivotal perceptivity. As we stand on the cliff of 2023, the exemplary notes from the dot-com bubble and the 2008 fiscal extremity echo loudly, prompting investors to approach unborn trends with perceptivity.
The US Stock Market historical Trend reveals a dynamic geography, shaped not only by profitable forces but also by the collaborative opinions of governments and the innovative winds of technology. It beckons investors to be watchful, adaptive, and forward-allowing. In this ever-evolving narrative, the literal trend of the US Stock Market is a roadmap.
It is a companion for investors, emphasizing the need to learn from history, acclimatize to the present, and cautiously anticipate the future. As we embark on the uncharted waters of market dynamics, understanding this historical trend is our stylish supporter for navigating the complications and misgivings that lie ahead.
FAQs [Frequently Asked Questions]
What is the historical performance of the US stock market?
Since its commencement in 1957, the indicator has shown a remarkable primary annualized average return of roughly 10.26% through the close of 2023. Although this figure may feel enticing, the critical factor lies in the timing of entering the market at a peak or exiting during a relatively low, which can significantly impact the enjoyment of similar returns. Timing becomes the crucial determinant in unleashing the complete eventuality of the seductive average number.
What is the history of the US stock market?
Originating in the 1800s, the AMEX, initially the “Curb Exchange,” got its name from market activities. Although its establishment is generally honored as 1921, the move to new quarters on triple that time solidified its founding date. The exchange’s early history is intertwined with its curbstone meetings, a distinctive feature that persisted until its relocation in 1921.
What is the stock market trend in 2023?
In 2023, investors witnessed a welcome resurgence in stock and bond market performance following a challenging 2022. Fueled by a robust economy, corporate earnings surpassing expectations, and signals of a halt in Federal Reserve interest rate hikes, stocks experienced a remarkable 25% rally during the year.
What are stock market trends?
A trend signifies the line of price movements, told by historical patterns. Comprising peaks and troughs, a market’s trend is determined by the direction of these high and low points. The upward, over, or sideways movement of these peaks and channels indicates the prevailing trend in the market.
Reference
- Dow Jones industrial average historical trends. Dow Jones Historical Trends Guggenheim Investments. (n.d.). https//www.guggenheiminvestments.com/advisor-resources/interactive-tools/dow-jones-historical-trends
- The expansion of the U.S. Stock Market, 1885—1930 Historical facts and … (n.d.). https//www.jstor.org/stable/23700715
- Market indexes Historical chart gallery. Market Indexes | Historical Chart Gallery | StockCharts.com. (n.d.). https//stockcharts.com/freecharts/historical/marketindexes.html
- The roaring twenties and the Great Depression – AP US history. TomRichey.net. (n.d.). https//www.tomrichey.net/twenties-and-depression.html
- S&P 500® index historical trends. S&P 500 Historical Trends | Guggenheim Investments. (n.d.). https//www.guggenheiminvestments.com/advisor-resources/interactive-tools/sp-500-historical-trends
- SoFi. (2023, November 8). A brief history of the stock market. https//www.sofi.com/learn/content/history-of-the-stock-market/